Windows SubSystem for Linux
In case if you are wondering, Windows Subsystem for Linux ( WSL) is a feature of Windows that allows you to run a Linux environment on your Windows machine.
I hate seeing the newline error as I switch between MacBook and Windows on a daily basis. Windows uses \r\n (CRLF) and macOS/Linux use \n(LF) line ending format. You could say I can add .gitattributes to my project root.
1
2
3
* text=auto eol=lf
*.py text eol=lf
*.txt text eol=lf
or force LF in .gitconfig
1
2
git config --global core.autocrlf false
git config --global core.eol lf
But the thing is Windows sucks. Don’t believe me, watch this
Enough with the BS, lets go back to WSL.
Basic commands for WSL
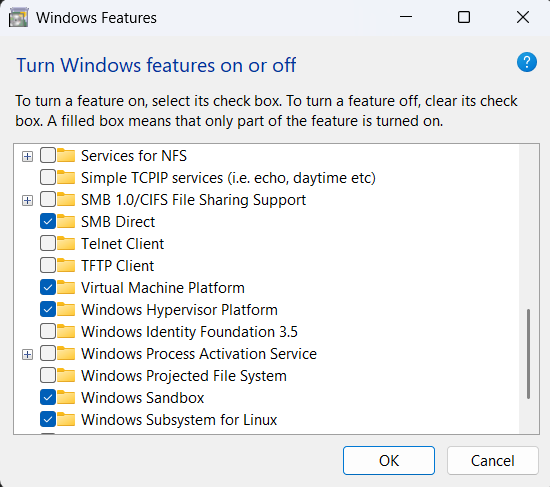
First make sure, the WSL and Virtual Machine Platform features are enabled.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
wsl --install # Install WSL with default Ubuntu distro
wsl --list --online # List available Linux distro
wsl --list --verbose # List installed distro
wsl --set-default <Distribution Name>
wsl ~ # Start WSL in user's home
wsl --distribution <Distribution Name> --user <User Name> #Run a specific Linux distribution from PowerShell or CMD
wsl --update # Update WSL
wsl --status # Check WSL status
wsl --version # Check WSL version
wsl --help
wsl --user <Username> #Run as a specific user
<DistributionName> config --default-user <Username> #Change the default user for a distribution
wsl --shutdown
wsl --terminate <Distribution Name>
1
2
3
4
# Identify IP Address
wsl hostname -I # Returns the IP address of your Linux distribution installed via WSL 2 (the WSL 2 VM address)
ip route show | grep -i default | awk '{ print $3}' #Returns the IP address of the Windows machine as seen from WSL 2 (the WSL 2 VM)
1
2
3
4
5
6
wsl --export <Distribution Name> <FileName> # Export a distribution
wsl --import <Distribution Name> <InstallLocation> <FileName> # Import a distribution
wsl --import-in-place <Distribution Name> <FileName> # Import a distribution in place
wsl --unregister <DistributionName> # Unregister or uninstall a Linux distribution
wsl --mount <DiskPath> # Mount a disk or device
wsl --unmount <DiskPath> # Unmount disks
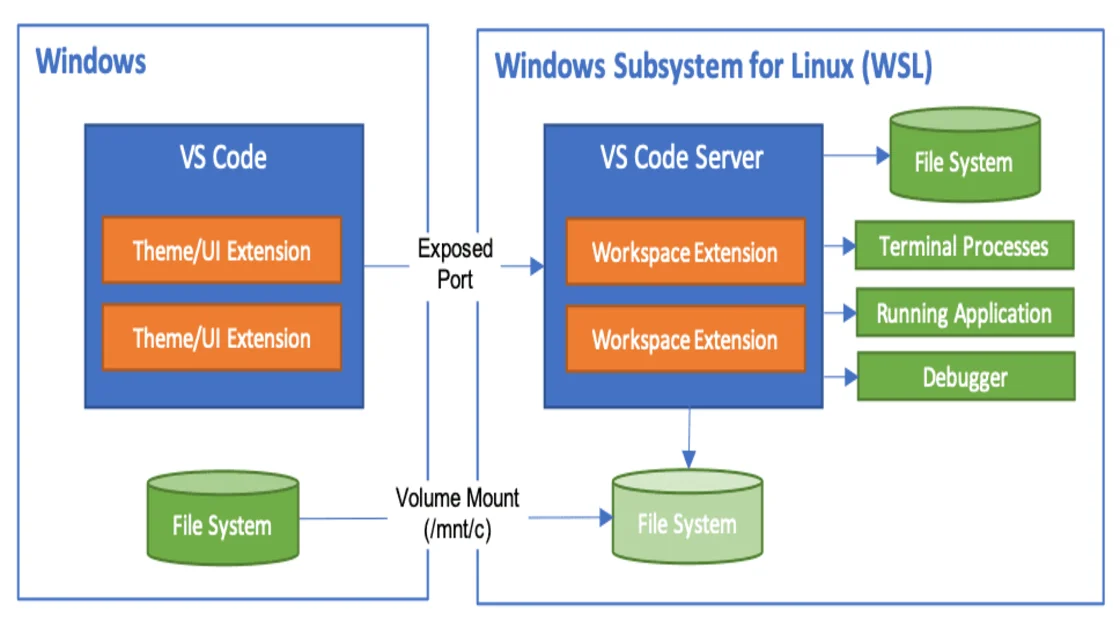
WSL and VS Code
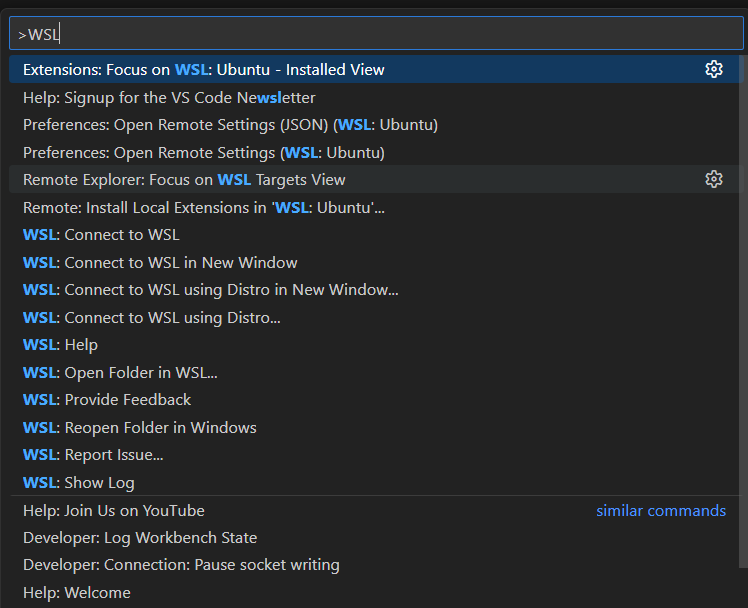
To access VS Code WSL option, from VS Code search (CTRL+SHIFT+P), search WSL
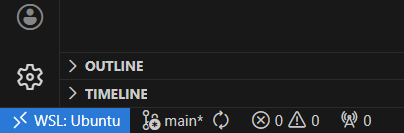
To confirm you are in WSL environment, plese check the bottom left corner, it should look something like this:
Summary:
- Start VS Code.
- Press F1, select WSL: Connect to WSL for the default distro or WSL: Connect to WSL using Distro for a specific distro.
- Use the File menu to open your folder.
From Windows command prompt
1
2
3
4
code --remote wsl+<distro name> <path in WSL>
# code --remote wsl+Ubuntu /home/satish/projects
# \\wsl.localhost\Ubuntu\home\butcher\repo
More about Developing in WSL
Reference:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/tutorials/wsl-vscode